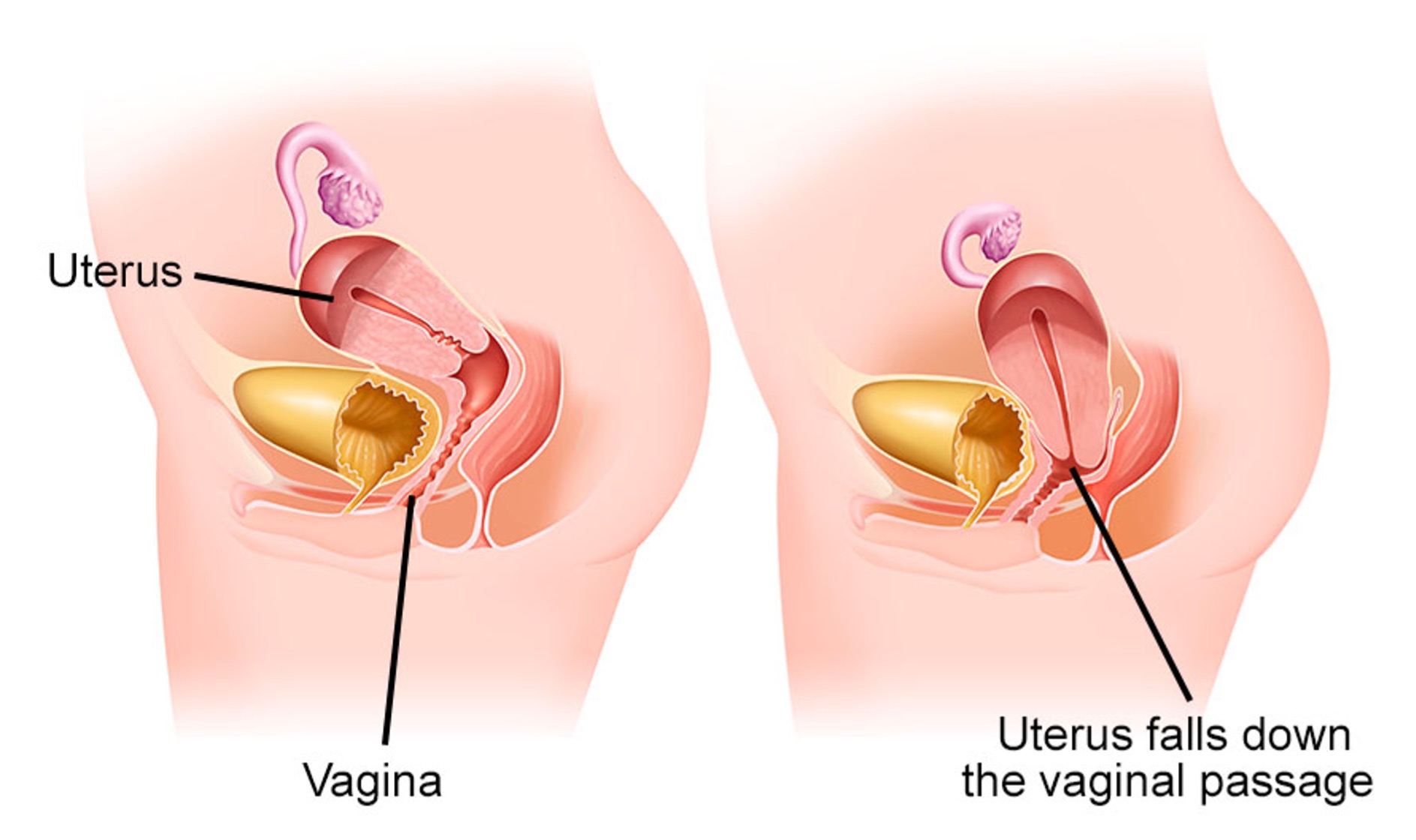
Pelvic organ prolapse refers to the anatomical disorder that occurs when a pelvic organ (bladder, rectum, uterus, or vaginal cuff in women who have undergone hysterectomy) descends through the vaginal wall.
This condition results from the weakening of the muscles and supporting structures of the pelvic floor, primarily caused by pregnancy and vaginal delivery. Age and menopause also play significant roles.
Prolapse affects many women, especially after menopause and particularly those with a history of vaginal births. In many cases, the condition may remain unnoticed for a long time, as symptoms can be absent. However, symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe and potentially dangerous issues, making specialized medical diagnosis and treatment essential.